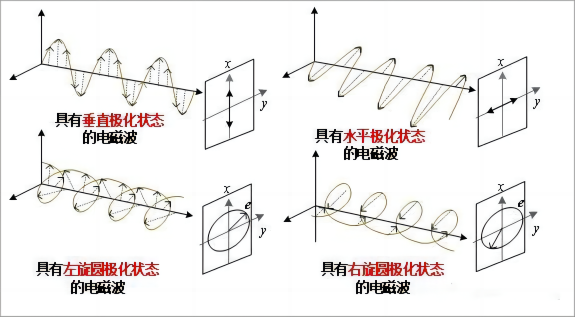
极化描述了电场矢量的尖端在波的传播期间建立的迹线。在远场,我们可以把电磁波看作平面波。在平面电磁波中,电场矢量和磁场矢量与传播方向正交并且也彼此正交。在一般情况下,电场矢量的尖端沿着椭圆螺旋线移动,即椭圆极化。如果电场矢量的尖端在传播时顺时针旋转,则称该波为右旋极化;否则它是左旋极化的。
Polarization describes the trace that the tip of the electrical field vector builds during the propagation of the wave. In the far field, we can consider the electromagnetic wave as a plane wave. In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electrical and the magnetic field vectors are orthogonal to the direction of propagation and also orthogonal to each other. In the general case, the tip of the electrical field vector moves along an elliptical helix, giving an elliptical polarization. The wave is called right-hand polarized if the tip of the electrical field vector turns clockwise while propagating; otherwise it is left-hand polarized.
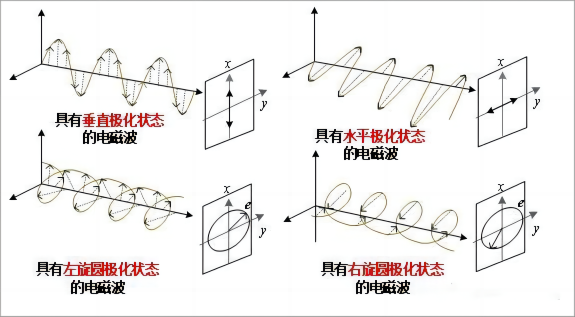
如果椭圆的两个轴具有相同的大小,则极化被称为圆极化。如果椭圆的两个轴中的一个变为零,则产生线极化,如果电场矢量垂直于地平面振荡则为垂直极化,如果其振荡方向平行于地平面则为水平极化。
If the two axis of the ellipse have the same magnitude, the polarization is called circular. If one of the two axis of the ellipse becomes zero, we have linear polarization, vertical if the electrical field vector oscillates perpendicularly to ground, horizontal if its direction of oscillation is parallel to the ground plane.
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文